We talked about much in the press about human cloning. In reality, the majority of scientists is not interested in producing human clones. What the scientists intend to do is to produce cloned human cells that could be used to cure some diseases. So how might work: imagine that you have a disease that is destroying parts of his brain slowly. Current treatments only reduce symptoms while the disease continues causing lesions in his brain. Cloning offers hope of cure. Scientists would produce a cloned embryo using DNA from their epidermal cells. Then they would withdraw this embryo stem cells, transforming them in brain cells and finally they transplantarían them to your brain. Cloning is a different way of using stem cells to cure certain diseases. Some people prefer this way of obtaining stem cells. In the end, a cloned embryo is a genetic copy of someone who is already alive and that gave their consent. It is obvious that we all have the right to decide what to do with our own DNA is not it? On the contrary, an embryo in the freezer of a fertilization clinic was created from the unique mixture of sperm and egg, and this is a union that will only happen once, producing a completely unique set of genes that have the potential to become a unique individual. And then, what is the best option?
Clonning True
viernes, 23 de octubre de 2015
domingo, 18 de octubre de 2015
Cellular cloning
Clone a cell consists of a group of them from a single. In the case of unicellular bacteria and yeast, this process is very simple and only requires the inoculation of suitable products. However, in the case of cultured cells in multicellular organisms, the cloning of cells is a difficult task, since these cells need the medium very specific conditions. A useful tissue culture technique used to clone distinct lineages of cells is the use of cloning (cylinders) rings. According to this technique, a grouping of unicellular cells that have been exposed to a mutagenic agent or a medicine used for the selection are put in a high dilution to create isolated colonies; each coming from a single potentially and clonally differentiated cell. In a first stage of growth, when the colonies have only a few cells; submerge sterile polystyrene fat rings, and put on a colony of single along with a small amount of trypsin. Cells that are cloned, are collected within the ring and is often a new container continue their growth in a natural way.
Molecular Cloning
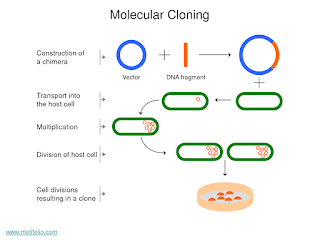
Molecular cloning is used in a wide variety of biological experiments, practical applications ranging from the taking of fingerprints to production of proteins on a large scale. In practice, in order to amplify any sequence in a living organism, the sequence cloned must be linked to an origin of replication; It is a sequence of DNA. Transfeccionse introduces the sequence formed inside cells. Seleccionfinalmente you select the cells that have been transfected with success with the new DNA. Initially, the DNA of interest need to be isolated from a segment of DNA of suitable size. Subsequently, the process of linking occurs when the amplified fragment is inserted into a cloning vector: vector are linearized (since is circular), using enzymes of restriction and then incubated under appropriate conditions the DNA fragment of interest and the vector with the enzyme DNA ligase. After the ligation of the vector with insert of interest occurs within cells Transfection, so the transfected cells were cultured; This process is the decisive process, since it is the part that we see if the cells were transfected successfully or not. We must therefore identify cells transfected and non-transfected, there are modern cloning vectors including markers of resistance to antibiotics that only cells that have been transfected can grow. There are other cloning vectors which provide blue / white screening. So, that investigation of the colonies is required to confirm that the cloning was successful.
What is the clonning?
It can be defined as the process by which are achieved, asexual way, 2 identical copies of an organism, cell or molecule already developed. The following characteristics should be taken into account: Firstly you need to clone the cells (embryonic product), that cannot be an organ or part of the "clone" If there is no with the cells that form the body. Be part of an agency already "developed", because cloning responds to an interest in getting copies of a particular organism, and only when it is adult characteristics can be known. On the other hand, is to create it in a way asexual.3 sexual reproduction does not get identical copies, since this type of reproduction by its very nature generates multiple
diversity.
diversity.
Suscribirse a:
Comentarios (Atom)