domingo, 18 de octubre de 2015
Molecular Cloning
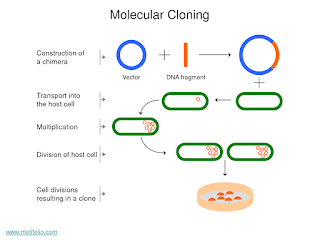
Molecular cloning is used in a wide variety of biological experiments, practical applications ranging from the taking of fingerprints to production of proteins on a large scale. In practice, in order to amplify any sequence in a living organism, the sequence cloned must be linked to an origin of replication; It is a sequence of DNA. Transfeccionse introduces the sequence formed inside cells. Seleccionfinalmente you select the cells that have been transfected with success with the new DNA. Initially, the DNA of interest need to be isolated from a segment of DNA of suitable size. Subsequently, the process of linking occurs when the amplified fragment is inserted into a cloning vector: vector are linearized (since is circular), using enzymes of restriction and then incubated under appropriate conditions the DNA fragment of interest and the vector with the enzyme DNA ligase. After the ligation of the vector with insert of interest occurs within cells Transfection, so the transfected cells were cultured; This process is the decisive process, since it is the part that we see if the cells were transfected successfully or not. We must therefore identify cells transfected and non-transfected, there are modern cloning vectors including markers of resistance to antibiotics that only cells that have been transfected can grow. There are other cloning vectors which provide blue / white screening. So, that investigation of the colonies is required to confirm that the cloning was successful.
Suscribirse a:
Comentarios de la entrada (Atom)
No hay comentarios.:
Publicar un comentario